
Rhinomanometry
Breathing is essential for survival.
A doctor may diagnose you with nasal obstruction based on your subjective account of nasal stuffiness and a limited physical examination demonstrating anatomic restriction of the nasal passages. Rhinomanometry is an objective test that measures the cause of high nasal resistence.
There are many causes of nasal obstruction:
Allergic rhinitis with turbinate hypertrophy
Anatomical nasal septum deviation, bone spur, or conchae bullosa
Sinus or nasal infection
Narrow palate
Four-Phase Rhinomanometry
Four- Phase Rhinomanometry is a non-invasive quantitative measurement of nasal airway function against a pressure gradient from which we can calculate nasal resistance.
Image Source: GM Instruments used, with permission
Four-Phase Rhinomanometry has many clinical uses. As an example, individuals are often recommended nasal surgery without objective confirmation of genuine mechanical obstruction. Measuring nasal obstruction using rhinomanometry before nasal surgery is vital because individuals with preoperative higher nasal resistances are more likely to benefit from the surgery.
Rhinomanometry Uses
Sleep Apnea
Investigate continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) intolerance due to high nasal resistance and assess for CPAP mask interface
OTC Allergy Treatment
Evaluate the decongestive action of antihistamines, corticosteroids, or nasal saline rinse
Rx Allergy Treatment
Evaluate allergy immunotherapy or antibiotic therapy efficacy and response
Children
Evaluate adenoids hypertrophy in children as young as three years old
Pre-Surgery
Individuals with preoperative high nasal resistances are likely to benefit from nasal surgery.
Post-Surgery
Individuals with postoperative low nasal resistances are likely to have benefitted from nasal surgery.
Rhinomanometry Examples
Visual guidance suggests whether airway resistance is within the normal, moderately obstructed, significantly obstructed, or severely obstructed range.
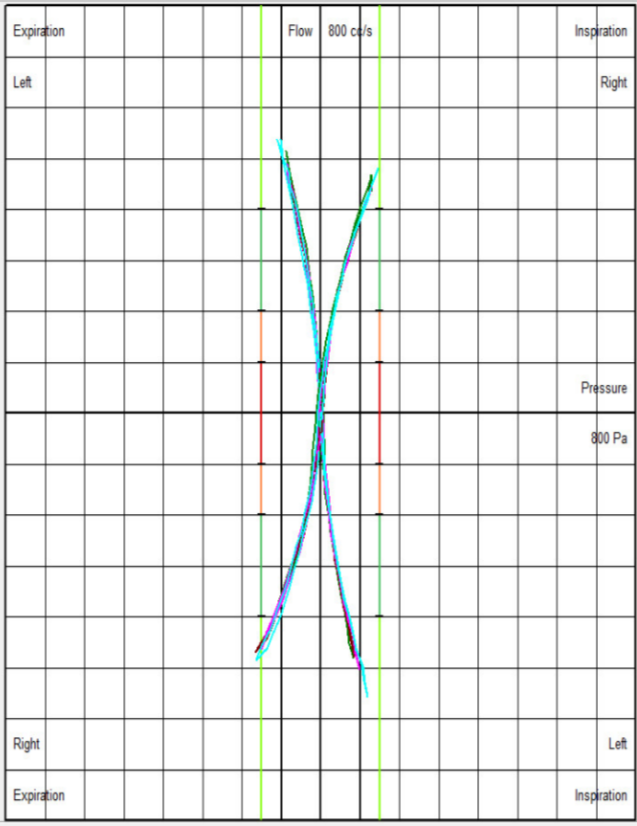
Normal Nasal Resistance
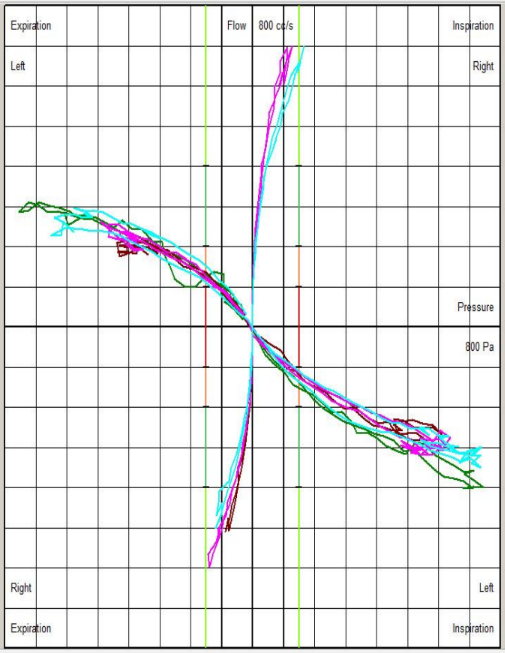
High Left Nasal Resistance
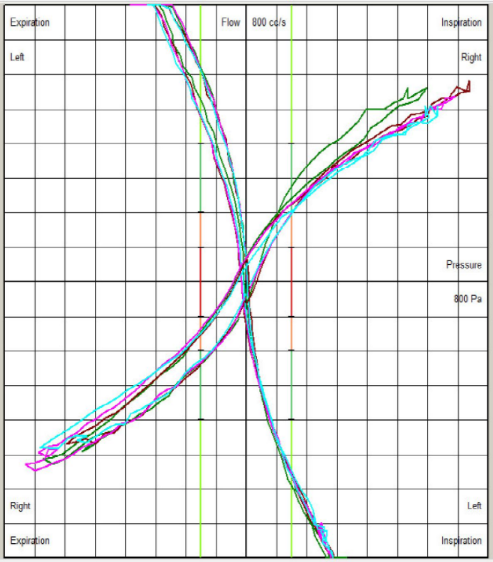
High Right Nasal Resistance
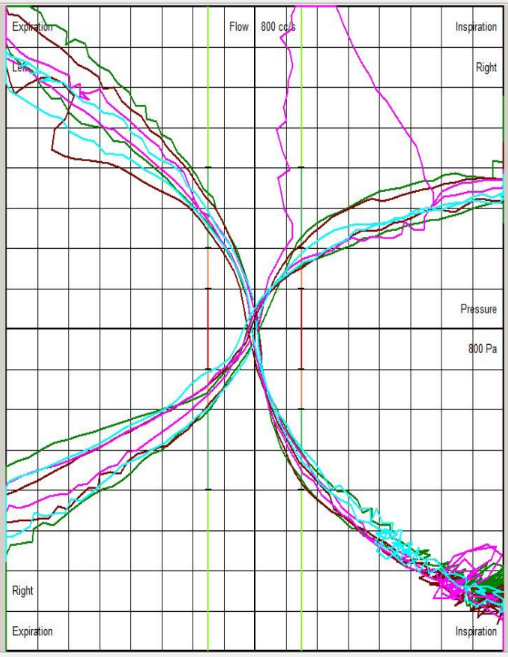
Child with High Left and Right Nasal Resistance

High Right>Left Nasal Resistance
Frequently asked questions
-
A standard exam or CBCT scan is a static image; it’s like looking at a parked car to see how fast it drives. Your nose might look "open" when you are sitting still, but the moment you inhale deeply, the side walls (nasal valves) may collapse inward due to the pressure change (the Bernoulli Effect). 4-Phase Rhinomanometry is a dynamic stress test. It measures how your nose behaves while it is working, often revealing "functional" obstructions that standard exams miss entirely.
-
Ascending Inspiration (The initial pull).
Descending Inspiration (The peak flow).
Ascending Expiration (The push out).
Descending Expiration (The relaxation). By mapping all four, we can calculate the Effective Diameter of your airway. If the lines on the graph separate widely (looping), it indicates that your nasal tissue is "floppy" and unstable, causing resistance that a CT scan cannot detect.
-
Absolutely. The nose accounts for 50% of the total resistance in your entire respiratory system. If your nasal resistance is too high (above 0.25 Pa/cm³/s), CPAP becomes physically intolerable because the machine has to fight too hard to push air through a narrow valve. This test gives us a precise numerical score for your resistance. If it is high, we know we must fix the nose before the CPAP will ever work comfortably.
-
MIP and MEP measures the strength of your Pump (Diaphragm and Intercostals). It tells us how much raw suction force your body can generate. Rhinomanometry measures the resistance of the nasal passages (The Nose). It tells us how much friction the air encounters as it enters.
It is common to find a patient with a "Ferrari Engine" (High MIP) who is failing because they are breathing through a "Straw" (High Nasal Resistance). We need both metrics to determine if your breathing failure is Muscular (Weak Pump) or Structural (Narrow Pipe).
-
It diagnoses the impact of allergies. We often perform this test twice: once at baseline, and once after applying a decongestant spray.
If your airflow improves dramatically after the spray, your obstruction is likely due to inflammatory causes (such as turbinate swelling/allergies).
If your airflow remains blocked after the spray, your obstruction is likely structural (due to bone/cartilage). This distinction prevents patients from wasting years on allergy shots for a problem that requires a mechanical fix.



